Since C is a structured language, it has some fixed rules for programming. One of it includes changing the size of an array. An array is collection of items stored at continuous memory locations.

As it can be seen that the length (size) of the array above made is 9. But what if there is a requirement to change this length (size). For Example,
- If there is a situation where only 5 elements are needed to be entered in this array. In this case, the remaining 4 indices are just wasting memory in this array. So there is a requirement to lessen the length (size) of the array from 9 to 5.
- Take another situation. In this, there is an array of 9 elements with all 9 indices filled. But there is a need to enter 3 more elements in this array. In this case 3 indices more are required. So the length (size) of the array needs to be changed from 9 to 12.
This procedure is referred to as Dynamic Memory Allocation in C.
Therefore, C Dynamic Memory Allocation can be defined as a procedure in which the size of a data structure (like Array) is changed during the runtime.
C provides some functions to achieve these tasks. There are 4 library functions provided by C defined under <stdlib.h> header file to facilitate dynamic memory allocation in C programming. They are:
- malloc()
- calloc()
- free()
- realloc()
Let’s look at each of them in greater detail.
C malloc() method
“malloc” or “memory allocation” method in C is used to dynamically allocate a single large block of memory with the specified size. It returns a pointer of type void which can be cast into a pointer of any form. It initializes each block with default garbage value.
Syntax:
ptr = (cast-type*) malloc(byte-size)
For Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
// This pointer will hold the
// base address of the block created
int* ptr;
int n, i;
// Get the number of elements for the array
n = 5;
printf("Enter number of elements: %d\n", n);
// Dynamically allocate memory using malloc()
ptr = (int*)malloc(n * sizeof(int));
// Check if the memory has been successfully
// allocated by malloc or not
if (ptr == NULL) {
printf("Memory not allocated.\n");
exit(0);
}
else {
// Memory has been successfully allocated
printf("Memory successfully allocated using malloc.\n");
// Get the elements of the array
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ptr[i] = i + 1;
}
// Print the elements of the array
printf("The elements of the array are: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("%d, ", ptr[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
- Output:
Enter number of elements: 5 Memory successfully allocated using malloc. The elements of the array are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,
C calloc() method
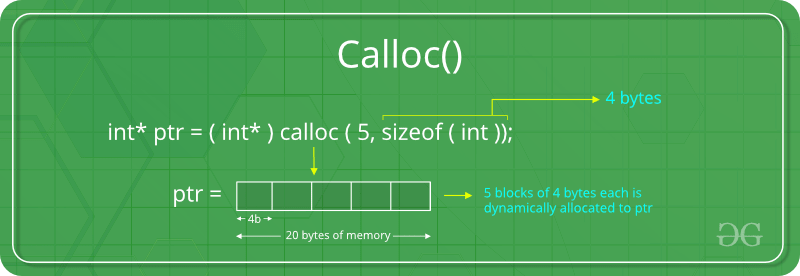
“calloc” or “contiguous allocation” method in C is used to dynamically allocate the specified number of blocks of memory of the specified type. It initializes each block with a default value ‘0’.
Syntax:
ptr = (cast-type*)calloc(n, element-size);
For Example:
ptr = (float*) calloc(25, sizeof(float));
This statement allocates contiguous space in memory for 25 elements each with the size of the float.
If space is insufficient, allocation fails and returns a NULL pointer.
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
// This pointer will hold the
// base address of the block created
int* ptr;
int n, i;
// Get the number of elements for the array
n = 5;
printf("Enter number of elements: %d\n", n);
// Dynamically allocate memory using calloc()
ptr = (int*)calloc(n, sizeof(int));
// Check if the memory has been successfully
// allocated by calloc or not
if (ptr == NULL) {
printf("Memory not allocated.\n");
exit(0);
}
else {
// Memory has been successfully allocated
printf("Memory successfully allocated using calloc.\n");
// Get the elements of the array
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ptr[i] = i + 1;
}
// Print the elements of the array
printf("The elements of the array are: ");
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
printf("%d, ", ptr[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
Comments
Post a Comment